Author Archives: Mohamed Abd Elhamid
How to Install Configuration Manager 2012 SP1 Clients on Linux Computers
You can accomplish this installation manually. Configuration Manager does not support the use of client push installation for Linux servers.
The following scenarios are supported by the Linux clients:
- Hardware Inventory – Hardware inventory can be viewed through Resource Explorer and can be used to create collections of Linux computers.
- Software Inventory – Through hardware inventory the list of natively installed software can be gathered from Linux computers – similar to add/remove programs for Windows systems.
- Software Distribution – Deploy new software, update existing software and apply OS patches to collections of Linux computers (using a package and program). Run arbitrary maintenance scripts on a collection of Linux servers.
- Secure and Authenticated Communications.
- Consolidated Reports.
The Microsoft System Center 2012 Service Pack 1 Configuration Manager – Clients for Linux
http://www.microsoft.com/en-sa/download/details.aspx?id=36212
- Download the appropriate file for the operating system you wish to manage to a Windows computer.
- The downloaded file is a self-extracting exe and will extract tar files for the different versions of your operating system.

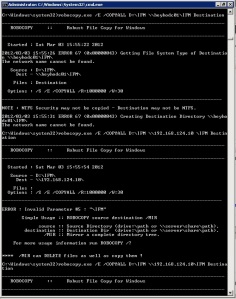
- Copy the install script and the .tar file for your computer’s operating system version to a folder on your Linux computer.
- Install the client using these steps:
- use root credentials to run the following command to enable the script to run as a program: chmod +x insta
- run the following command to install the Configuration Manager client: ./install –mp <hostname FQDN> -sitecode <code> ccmRHEL5x86.tar
Group policy search tool (GPS)
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
GPS is a online group policy search tool for Microsoft Active Directory Group Policy Settings.
You are unsure whether a policy for your setting exists. you have ever tried to find the registry setting for a specific group policy setting.
With the help of Group Policy Search you can easily find existing Group Policies and find the registry setting for a specific group policy
Group Policy Search will give you what you need. Try it Here
- GPS page overview
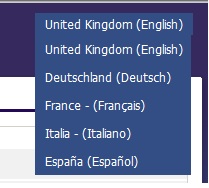
- You can change the display and search language
- You can change Tree view (policy view or Registry view)
- You can filter the search to specific products and/or versions
- You can share using the one-click copy feature in the copy menu

- You can add a Search Provider and a Search Accelerator for your Internet Explorer or a Search Connector for your Windows 7
How to Repair Windows System Files with System File Checker (SFC)
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
What is System File Checker (SFC)?
System File Checker is a utility in Microsoft Windows that allows users to scan for and restore corruptions in Windows system files like DLL files. This utility is available in all Windows family of operating systems.
In Windows 7, System File Checker is integrated with Windows Resource Protection, which protects registry keys and folders as well as critical system files.
How to use SFC
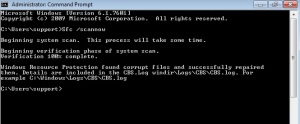
1- Start – Search – type Cmd – right click Cmd icon and run as administrator
2- Type SFC /Scannow then Enter
Important:
- You must run Command Prompt as an administrator in Windows 7.
- If it finds a problem, it will attempt to replace the problematic files from the DLL Cache
- If the file is not in the DLL Cache or the DLL Cache is corrupted you may need access to your original Windows DVD to allow file repairs.
- To repair important Windows files usually takes 5 to 10 minutes.
- May be prompt you to restart.
3- When the scan is complete. The log file was generated in the path
C:\Windows\Logs\CBS\CBS.log
How to install Windows 8 Developer Preview
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
– What is Windows 8 Developer Preview?The Windows 8 Developer Preview is a pre-beta version of Windows 8 for developers and testers.
System RequirementsThe Windows 8 Developer Preview works great on the same hardware that powers Windows Vista and Windows 7:
- 1 gigahertz (GHz) or faster 32-bit (x86) or 64-bit (x64) processor
- 1 gigabyte (GB) RAM (32-bit) or 2 GB RAM (64-bit)
- 16 GB available hard disk space (32-bit) or 20 GB (64-bit)
- DirectX 9 graphics device with WDDM 1.0 or higher driver
- Taking advantage of touch input requires a screen that supports multi-touch
- To run Metro style Apps, you need a screen resolution of 1024 X 768 or greater
1- Download Windows 8 Developer Preview from here
2- Burn iso file to DVD or we can install it in VMware Workstation 8 but when select system you will choose windows 7 because VMware
Workstation 8 not support Windows 8 Developer Preview directly )
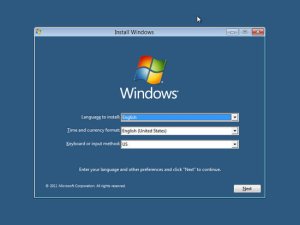
3- boot from DVD.
4- After booting.
5- Select your Language, Time and Currency Format and Keyboard or input method.
 6- You can select Upgrade or Custom (i prefer custom)
6- You can select Upgrade or Custom (i prefer custom)
 7- select partition and click next.
7- select partition and click next.
8- Just wait untill installing finshed and system restarting
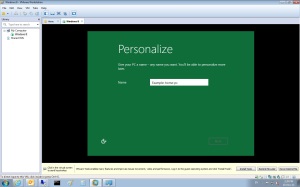
9- Type computer name and click Next.
10- Click Express Settings or Customize.
11- There are two ways to use an account in Windows 8 Windows Live Account or Local account we will select local account
13- This Metro UI Appearance click Desktop Icon to go your Desktop
Metro UI fantastic with touch screen
How to Prevent Authenticated Users from joining Workstations to a Domain
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
I asked myself what is benefit from this option “by default, Windows Server allows authenticated users to join 10 machine accounts to the domain”. But I didn’t get an answer
Administrator can control it with two ways:
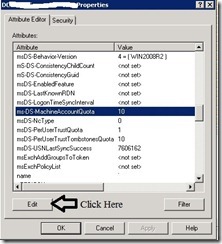
1-By Adsiedit:
- Start – Administrative Tools – ADSI Edit
- Right click Domain Name – Properties
- Attribute Editor Tab – ms-DS-MachineAccountQuota – Click Edit – set to 0 –press ok
Note:
That users in the Administrators or Domain Administrators groups, and those users who have delegated permissions on containers in Active Directory to create and delete computer accounts, are not restricted by this limitation.
2-By Group Policy:
- Click Start – All programs – Administrative Tools – Group Policy Management.
- Create or Edit Group Policy Objects.
- Expand Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – User Rights Assignment
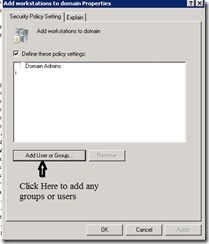
- From right pane right click on Add workgroup to domain – Properties – Add User or Group or remove unwanted user or group
How to configure AppLocker Group Policy to prevent software from running
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
Firstly: What is AppLocker?
AppLocker is a set of Group Policy settings that evolved from Software Restriction Policies, to restrict which applications can run on a corporate network, including the ability to restrict based on the application’s version number or publisher.
- Click Start – All programs – Administrative Tools – Group Policy Management.
- Create or Edit Group Policy Objects.
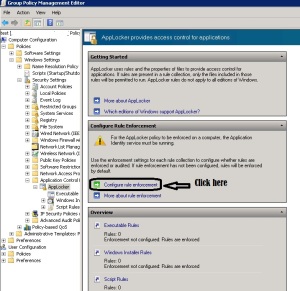
- Expand Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Application Control Policies – AppLocker .
- In right pane click on Configure rule enforcement
Note:
-
Executable rules: .exe, .com
-
Windows Installer rules: .msi, .msp
-
Scripts rules: .ps1, .bat, .cmd, .vbs, .js
- Under Executable rules check configured box and select Enforce rules then click ok

- In left pane under AppLocker right click on Executable Rules then select Create New Rule
- Select Deny and select what user or group will prevent.
Note:
Publisher rules: This condition identifies an application based on its digital signature and extended attributes. The digital signature contains information about the company that created the application (the publisher). The extended attributes, which are obtained from the binary resource, contain the name of the product that the application is part of and the version number of the application.
Path rules: This condition identifies an application by its location in the file system of the computer or on the network.
File hash: This condition identifies an application which is not digitally signed can be restricted by a file hash rule instead of a publisher rule.
- Select Publisher and click Next

- Click browse then select executable file example.exe
- Choose any options from prevent with any publisher, publisher, product name, file name and file version then click Next.
- Read it and click Next

- Click Create

- You will now be prompted to create some default rules that ensure that you don’t accidently stop Windows from working. Click “Yes” to this if you don’t already have these rules created.
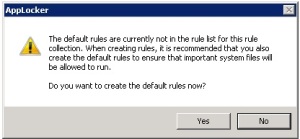
Note:
If you want to apply this role on computer administrator then right-click on the BUILTIN\Administrators rule and click Delete
Now we will active the Application Identity service to enable AppLocker on the computers
- In the same Group Policy Object you were just editing Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – System Services
- Right click Application Identity service then properties
- Check Define this policy setting box and Automatic then OK.

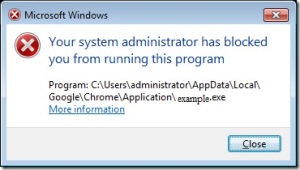
Now when users try run program he will get this
Reference:
http://www.windows7library.com/blog/security/applocker-part-2-understanding-applocker-rules/
How to force proxy settings via group policy
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
This article describes how to force proxy settings via group policy.
- Click Start – All programs – Administrative Tools – Group Policy Management.
- Create or Edit Group Policy Objects.
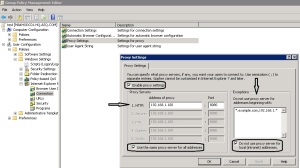
- Expand User configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Internet Explorer Maintenance – Connection.
- In right Pane Proxy Settings.
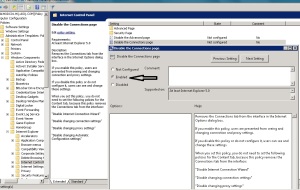
For some security reasons maybe administrator need to prevent end users from change their proxy settings
You can do it with group policy follow this steps:
How to Find the MAC Address
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
This article describes a quick method to find the MAC Address(Media Access Control).
1- What is MAC Address ?
– A Media Access Control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces
for communications on the physical network segment.
2- What is ARP?
– Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is the protocol that maps Ethernet MAC address to IP address.
To determine the MAC address of computer:
start – Run – type ARP -a (local computer IP)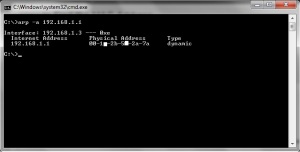
Note : If you not determine the IP the command will give you MAC Address for all subnet network.